Identifying the Issue
- The presence of toxic ionic pollutants such as mercuric (Hg²⁺) and nitrite (NO2−) ions in water sources pose significant environmental and health concerns.
- Although various nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensors have been developed for individual ion detection, dual-ion sensing platforms remain scarce.
Objective of the Research
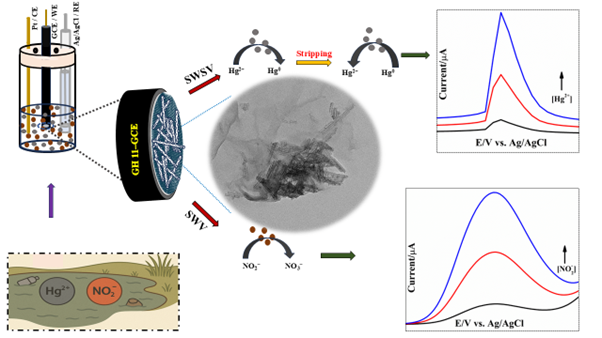
- Develop an efficient dual-function electrochemical sensor for the simultaneous detection of Hg²⁺ and NO2− ions in water using a nanocomposite of graphene oxide and hydrogen titanate nanotubes.
Who should read this?
- Environmental scientists, researchers, and engineers – Developing advanced nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensing platforms for real-time detection of chemical water contaminants.
- Water treatment industries and policymakers – Implementing integrated sensing platforms for improved water quality monitoring and regulation.
Solution
A novel electrochemical sensor of graphene oxide-hydrogen titanate nanotubes nanocomposite for simultaneous detection of both mercuric (Hg²⁺) and nitrite (NO₂⁻) ions in aqueous systems.
Key Features and Benefits
- Time & Cost-efficient: Simultaneous detection of two pollutants in a single test reduces resources, analysis time, and
- Dual-Ion Sensing Capability: Measures both cationic (Hg²⁺) and anionic (NO₂⁻) contaminants, enhancing the scope of water quality assessment.
- Environmentally Relevant: Facilitates early detection of toxic contaminants, preventing ecological damage and human exposure risks.
Impact
- Enhances Water Safety: Accurately detects Hg²⁺ and NO₂⁻ at low concentrations, ensuring safe drinking.
- Improves Monitoring Efficiency: Enables simultaneous multi-ion detection, reducing testing time by over 50% compared to conventional single-ion analysis methods.
Team
- Dasari Swarna
- Lokeswara Reddy S
- Sushma Tripathi
- Anjana Biswas
- Ganesh V (Corresponding author)
- Prathibha C (Corresponding author)
Title of paper: “A dual-target electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of mercuric and nitrite ions in water using a nanocomposite of graphene oxide and hydrogen titanate nanotubes”
Read Paper Here: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2025.115488